Management Accounting
Last Update 3 days ago
Total Questions : 260
CIMA Operational is stable now with all latest exam questions are added 3 days ago. Incorporating P1 practice exam questions into your study plan is more than just a preparation strategy.
P1 exam questions often include scenarios and problem-solving exercises that mirror real-world challenges. Working through P1 dumps allows you to practice pacing yourself, ensuring that you can complete all CIMA Operational practice test within the allotted time frame.
A special contract requires 640 units of component T.
The inventory of 280 units of component T cost $0.20 per unit but the component is not currently used by the company.
The current market price of component T is $0.24 per unit but the inventory could be sold for $0.15 per unit.
The relevant cost of the units of component T required for the special contract is:
A company manufactures a single product. The company absorbs fixed production overhead using a pre-determined rate per unit.
The following data applies for month 7:
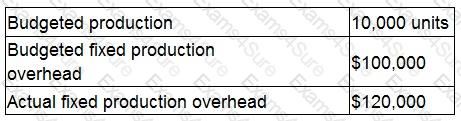
During month 7 fixed production overhead was over absorbed by $40,000.
What was the actual number of units produced during month 7?
Which TWO of the following statements are true for obtaining a reliable forecast from a time series?
ABC uses an activity-based costing system.
The company manufactures three products, details of which are given below:
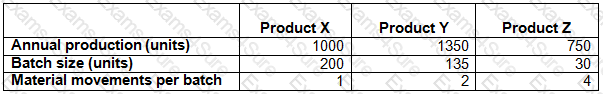
Total material movement costs for the period are $10,000.
The material movement cost per unit for Product Z (to the nearest $0.01) is:
A manager is deciding which one of four services to provide next period.
The contribution earned by each service will depend on the weather conditions as follows.
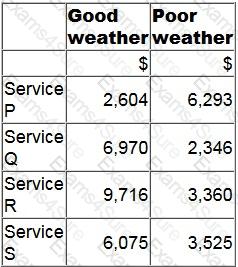
Using the maximin criterion, which service will the manager provide?
The following statements relate to the advantage(s) that linear regression has over the high-low method in the analysis of cost behaviour:

Which statement(s) is/are true?
MBM is considering introducing a new product and has to decide if the sales price should be $80, $90, $100 or $120.
There is a 30% chance that demand could be high, a 50% chance that demand will be at a medium level and a 20% chance that demand will be low.
A payoff table below shows the profits based on the sales price and the level of demand.
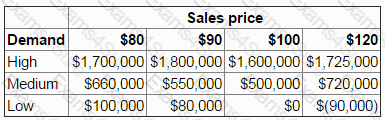
MBM has decided, using an expected value approach, that the sales price should be set at $80 as this gives the highest expected profit of $860,000.
A market research company has since approached MBM offering to provide perfect information on the demand level.
What is the maximum amount that should be paid for the perfect information?
Give your answer as a whole number (in '000s).
A company has only 10,100 hours of skilled labour available next period.
Data for its three products for next period are as follows.
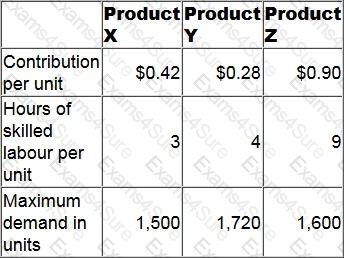
At least 500 units of each product must be sold each period.
No inventories are held.
How many units of Product X should be manufactured next period in order to maximise profit?


TESTED 29 Oct 2025
Hi this is Romona Kearns from Holland and I would like to tell you that I passed my exam with the use of exams4sure dumps. I got same questions in my exam that I prepared from your test engine software. I will recommend your site to all my friends for sure.
Our all material is important and it will be handy for you. If you have short time for exam so, we are sure with the use of it you will pass it easily with good marks. If you will not pass so, you could feel free to claim your refund. We will give 100% money back guarantee if our customers will not satisfy with our products.