Fundamentals of management accounting
Last Update 5 days ago
Total Questions : 392
Fundamentals of management accounting is stable now with all latest exam questions are added 5 days ago. Incorporating BA2 practice exam questions into your study plan is more than just a preparation strategy.
BA2 exam questions often include scenarios and problem-solving exercises that mirror real-world challenges. Working through BA2 dumps allows you to practice pacing yourself, ensuring that you can complete all Fundamentals of management accounting practice test within the allotted time frame.
A company’s management accountant wishes to calculate the present value of the cost of renting a delivery vehicle. There will be five annual rental payments of $5,000, the first of which is due immediately. The company’s discount rate is 12%.
Which TWO of the following are valid ways to calculate the present value of the rental payments? (Choose two.)
The following data are available for a company that produces and sells a single product.
The company’s opening finished goods inventory was 2,500 units.
The fixed overhead absorption rate is $8.00 per unit.
The profit calculated using marginal costing is $16,000.
The profit calculated using absorption costing and valuing its inventory at standard cost is $22,400.
The company’s closing finished goods inventory is:
A sales manager has analysed a sample of 350 sales transactions from the latest period. The manager wishes to investigate:
how many customers made their purchase online using the internet and how many purchased by telephone.
how many were new customers and how many were placing repeat orders.
The following table shows the results of the analysis.
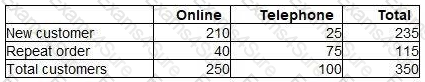
If the pattern of sales occurs next period, the probability of a particular sale being a repeat order placed online is closest to:
A project is about to be launched. Two of the three possible outcomes and their associated probabilities are as follows:
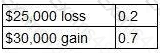
The remaining possible outcome is a $70,000 gain.
What is the correct calculation of the expected value of the project?
In a company that manufactures many different products on the same production line, which TWO of the following would NOT be classified as indirect production costs? (Choose two.)
Which THREE of the following are included in the Global Management Accounting Principles? (Choose three.)
An organisation produces and sells a single product. The organisation’s management accountant has reported the following information for the most recent period.
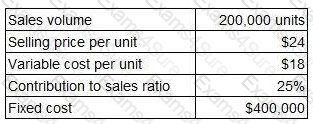
Which TWO of the following statements are valid? (Choose two.)
The following is an extract from a budgetary control report for the latest period:
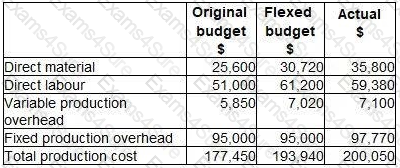
The budget variance for prime cost is:
The possible returns and associated probabilities of two independent projects are as follows:
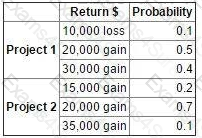
It has been decided that both projects are to be launched.
Which TWO of the following statements are correct? (Choose two.)


TESTED 27 Jul 2024
Hi this is Romona Kearns from Holland and I would like to tell you that I passed my exam with the use of exams4sure dumps. I got same questions in my exam that I prepared from your test engine software. I will recommend your site to all my friends for sure.
Our all material is important and it will be handy for you. If you have short time for exam so, we are sure with the use of it you will pass it easily with good marks. If you will not pass so, you could feel free to claim your refund. We will give 100% money back guarantee if our customers will not satisfy with our products.